Symptoms
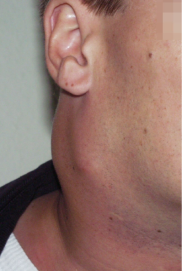
In most cases the first clinical sign of Hodgkin lymphoma is a painless, rubber-like swelling of the lymph nodes. It typically appears on the neck (in approx. 70% of cases) and, more rarely though, the lymph nodes above the collarbone, in the armpits or in the groin region may be affected.
About one third of Hodgkin lymphoma patients develop a lymph node swelling behind the breastbone (mediastinal lymph nodes), which may disturb breathing and cause a feeling of pressure and continuous coughing.
Sometimes only single abdominal lymph nodes are involved, which may lead to abdominal pain, a feeling of pressure or diarrhea.
The consumption of alcoholic beverages may cause pain in the involved lymph nodes, which is a very rare but rather typical characteristic of Hodgkin lymphoma.
About one third of affected patients show unspecific common symptoms like a decreased general performance, tiredness, weakness and strong itching all over the body.
In the diagnosis of the disease, special attention should be paid to the presence or absence of the so-called Bsymptoms. They are considered as stage-defining factors and are therefore directly related to the choice of therapy.
B-symptoms include:
- Severe night sweats (linen needs to be changed)
- Unintended weight loss of more than 10% of the total body weight during the last six month
- Fever of over 38°C with changing course and unknown origin.
The increasing number of tumor cells in the lymph nodes disturbs and weakens the balance of the immune system. This may lead to frequent bacterial, viral or fungal infections. If the disease has spread outside the lymph nodes to other organs like bones or liver, this may cause further symptoms and complaints. If bones are affected, pain in the bones and frequent fractures are typical signs. A bone marrow infiltration may lead to changes in the blood count. The liver may become enlarged if it is involved, causing pressure or pain in the upper abdomen and changes in the hepatic and biliary laboratory parameters.